Invoice fraud exposed: tips for spotting fake invoices
Corcentric

Imagine your business suddenly hemorrhaging cash, not from poor sales or market downturns, but because a criminal has slipped a bogus invoice into your stack. Invoice fraud is an insidious threat that chips away at a company’s financial foundations. Understanding what it is and how it manifests is the first line of defense.
Every year, Accounts Payable (AP) organizations of all sizes face the dire consequences of invoice fraud, which can range from minor financial losses to substantial legal troubles. Before you approve that next payment, consider the realities of a world where scammers are constantly refining their deceitful art.
Understanding invoice fraud
Invoice fraud strikes by exploiting invoicing processes with fake or modified billing documents. In what masquerades as a regular transaction, fake invoices are meticulously crafted to mimic legitimate requests for payment, but they channel business funds into fraudster-operated bank accounts. These schemes often rely on slight variances from standard documents—bogus bank details, altered email addresses, and phony vendor information—that go unnoticed until the financial damage surfaces. These malicious alterations are regularly overlooked due to human error or the high volume of incoming invoices processed by businesses. Moreover, invoice fraud can persist undetected over long stretches, exacerbating the problem.
Common types of invoice fraud
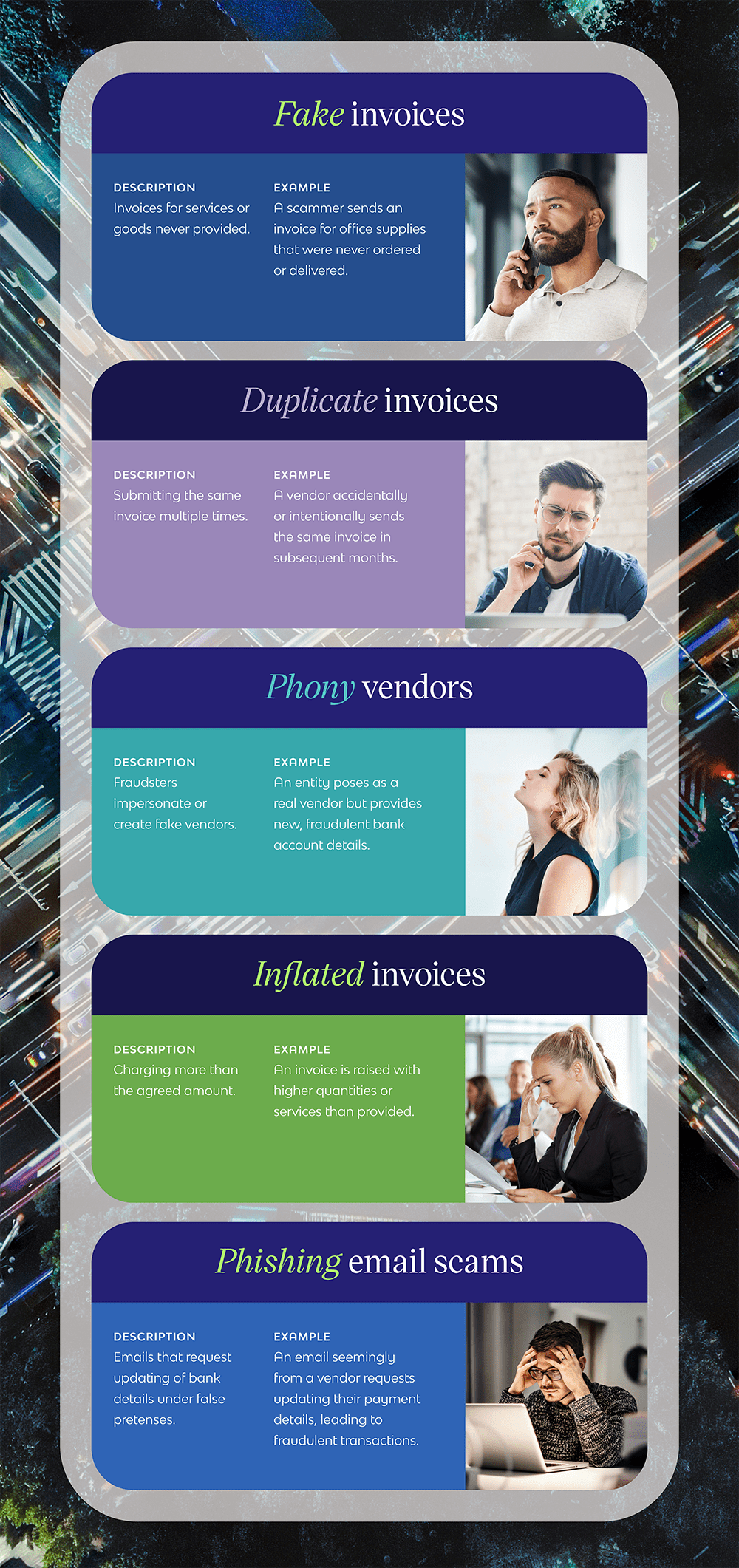
The landscape of invoice fraud is marked by several prevalent types:
- Fake invoices: Invoices for services or goods that were never actually provided.
- Duplicate invoices: Submitting the same invoice multiple times can also be a common tactic used by fraudsters.
- Phony vendors: Fraudsters impersonate or create fake vendors to trick businesses into making payments to nonexistent or fraudulent entities.
- Inflated invoices: Charging more than the agreed amount is another tactic used to deceive businesses by adding inflated charges or unauthorized fees.
- Phishing email scams: Sending deceptive emails that appear to be from legitimate businesses or vendors.
Take a look at these specific examples:
A staggering statistic reveals the extent of the problem: 20% of fraud cases analyzed involved invoice schemes, with median losses of a staggering $125,000. This affects businesses both big and small, with bigger businesses being more prone to communication breakdowns between departments, and smaller businesses having looser verification processes.
Consequences of invoice fraud
The impact of invoice fraud cuts deep and extensive: way beyond the immediate financial setbacks. The ordeal could result in legal entanglements, hefty fines, rigorous audits, or even criminal charges leading to imprisonment or confiscation of assets. This can lead to legal scrutiny, damaged reputations, and threaten an organization’s existence. Invoice fraud can sour relationships with genuine vendors when payments don’t reach them as anticipated, believing their invoices had been settled. The chaos of integrating fraudulent records into accounting systems can lead to clerical nightmares as well.
Identifying fraudulent invoices
Invoice fraud begins by infiltrating the once-trusted communication channels between a vendor and their client. Spotting invoice fraud is not easy.
Suspicious invoice characteristics
Here are some telltale signs to look for in fraudulent invoices:
- Poor English or grammar
- Lack of personalization (‘Dear customer’ vs. a specific contact name)
- Unusual phrasing or language choices
- Generic email templates
- Discrepancies in email addresses or contact details
Checking the legitimacy of an invoice
Assurance of authenticity requires due diligence by an Accounts Payable department. Begin by scrutinizing key invoice components: the invoice date, the email address it was sent from, the precision of contact information, and the exactness of bank account numbers and details. Next, compare the invoice with the finance team’s records. Are the amounts charged in line with past services or goods procured? Does the dollar figure deviate significantly from the norm? Formatting eccentricities – different tabulating methods or unusual font choices, for instance – can also raise suspicion. Verify that each item listed was indeed purchased; any inclusion of items not procured should sound alarm bells.
Verifying bank account details
The safeguarding against altered bank information, a favored tactic of scammers, is a critical internal control measure. Establish robust protocols for not just verifying new vendor details, but also for managing changes to existing ones. Implement a combination of checks, such as:
- Two or three-way matching, aligning invoices with purchase orders and delivery receipts
- Regularly updated authorizations for who can approve changes to banking information
- Direct communication with vendors through verified channels when alerted to changes in payment details
By strong adherence to these protocols, businesses can significantly decrease the likelihood of falling prey to the sophisticated traps laid by invoice fraud schemes.
Preventing invoice fraud
Preventing invoice fraud requires a culture of vigilance and employs strategic safeguards across several operational areas. By honing in on key prevention strategies, businesses can erect a formidable barrier against the persistent threat of invoice manipulation. Here are some vital practices:
Implement stronger internal controls
To reinforce the fortress guarding a company’s finances, robust internal controls are imperative. Incorporate checks and balances in the accounts payable process to necessitate multiple signoffs for substantial transactions. Use automation tools like Corcentric StopFraud to enforce controls at scale. This mitigates the risk posed by having a solo individual dominate the ordering, approval, and payment sequence.
Train employees to recognize red flags
A well-informed workforce is an organization’s first line of defense against fraud. Conduct regular training sessions to keep employees abreast of the latest fraud tactics and the consequential red flags that emerge. Tailor the training to address role-specific vulnerabilities, ensuring finance teams are adept at intricate invoice verifications while IT units fortify cybersecurity defenses.
Regularly review and compare invoices
Diligent invoice scrutiny is a staple in the anti-fraud diet. Regular reviews to spot discrepancies in the information, such as altered vendor contact or payment addresses, are critical. Compare current invoices against previous records stored in the enterprise resource planning (ERP) system to verify consistency in payment details.
Anomalies in invoice images and other specifics, in contrast with ERP data, should prompt further investigation. Assuring the alignment of incoming invoices with actual services rendered or goods received steers clear of false billing. The commitment to continuous supervision and comparison of invoices is indispensable in pinpointing and, ultimately, protecting against invoice fraud.
Reporting and responding to invoice fraud incidents
When faced with a case of invoice fraud, it’s critical to act swiftly and decisively. Notifying the relevant financial institutions should be a priority to prevent further transactions related to the fraudulent invoice. Businesses should contact their bank or credit card company immediately to halt any payments and begin the process of recovering lost funds.
As the reporting process unfolds, consider convening a meeting with your financial and legal teams to understand the implications of the fraud. If you fall prey to an invoice fraud scheme, legal assistance may become necessary. Companies may face civil or criminal legal actions, so having the guidance of an experienced business or criminal defense attorney is paramount. These professionals can navigate the complexities of the law and advocate on your business’s behalf.
Implementing security measures to prevent invoice fraud
Once immediate actions have been taken, businesses should focus on running internal audits to identify any internal vulnerabilities that may have been exploited by the fraudsters. Addressing these weaknesses is crucial for preventing future occurrences and safeguarding the organization’s financial integrity. Additionally, efforts should be made to reinforce security measures. Training staff about the identification of fake invoices, clarifying communication lines with suppliers, and injecting automation into accounting processes are all strategic steps towards achieving a more secure financial operation post-incident.
Recovering losses and strengthening security measures
When dealing with invoice fraud, it is important to take immediate and considered actions. Begin by notifying banks and legally reporting the fraud to initiate recovery actions. Conduct interviews with legal privilege to maintain confidentiality and build a defense if necessary. Introduce stricter approval processes for high-value invoices and directly confirm any changes in vendor information. File a report with relevant government institutions to aid in the investigation and prevent future scams. After recovering, reassess systems to identify vulnerabilities and implement updated checks and balances to reinforce your defenses against future attempts at invoice fraud.
At Corcentric, we have a StopFraud validation solution which includes a 12-step verification process to limit the risk of invoice fraud. Our team provides monitoring to ensure payments are delivered successfully every time, verifying vendor information, and flagging suspicious transactions. This solution helps businesses mitigate financial risks, enhance compliance, and ensure the integrity of their accounts payable processes., verifying vendor information, and flagging suspicious transactions. This solution helps businesses mitigate financial risks, enhance compliance, and ensure the integrity of their accounts payable processes.